SAP Password Security – 10 years later

Chapters
Share Article
Let's Talk SAP Security
Have questions about SAP Security? We’re here to help. Contact Us
It has been 10 years since I wrote a blog post on the SAP Community Network about the risks of old and insecure password hashes and overall password security in SAP systems. Let’s take a look back and see what has changed in terms of SAP password security over the past decade.
More awareness and action in the SAP ecosystem for password security
The above-mentioned blog specifically raised concerns about password security, specifically on the use of old and insecure password hashes, known as BCODE password hashes, commonly found in many customers’ SAP systems in the USR02 table at the time. With the released version of Hashcat, an offline password-cracking tool, it became easy to compromise password security by brute-forcing SAP password hashes into plaintext passwords.
If you have a few spare minutes, I suggest (re)reading the blog, as it describes the basics of password cracking and provides a better understanding of the mechanism behind passwords. This is especially relevant because we sometimes still encounter these insecure password hashes, and the tools to perform password cracking are freely available to anyone on the internet. Back in 2014, the use of insecure password hashes was still widespread.
But much has changed since then, for the better!
Over the past decade, we have observed that many customers are much more SAP Security-aware and have proactively removed the BCODE hashes. SAP has introduced the program CLEANUP_PASSWORD_HASH_VALUES, and an even better alternative, ZCLEANUP_PASSWORD_HASH_VALUESX, to help remove old and insecure password hashes.
SAP has also introduced more modern and stronger password hashing algorithms. These algorithms are much stronger and brute-forcing them takes considerably more time than the older, insecure versions. The PWDSALTEDHASH algorithm is currently the strongest. This greatly helps prevent SAP credentials from getting compromised when access to password hashes is obtained.
In addition, we see significant improvements in general password security and password parameters. F, SAP’s default password length was set to 6 characters for a long time, but for most of our customers, this is now at least 8 or more characters. See help.sap.com for more details. Access to password hash tables such as USR02 and USH02 has also been restricted..
Even though our SecurityBridge customer base may not represent the complete SAP customer population, we are seeing a lot of traction in the SAP Security topic more broadly, particularly when attending SAP user group events. We are happy to see the growing focus on security. Additionally, we see that our customers are becoming more mature and have better hardened their SAP systems on the topics mentioned above. For example, around password hash algorithms:
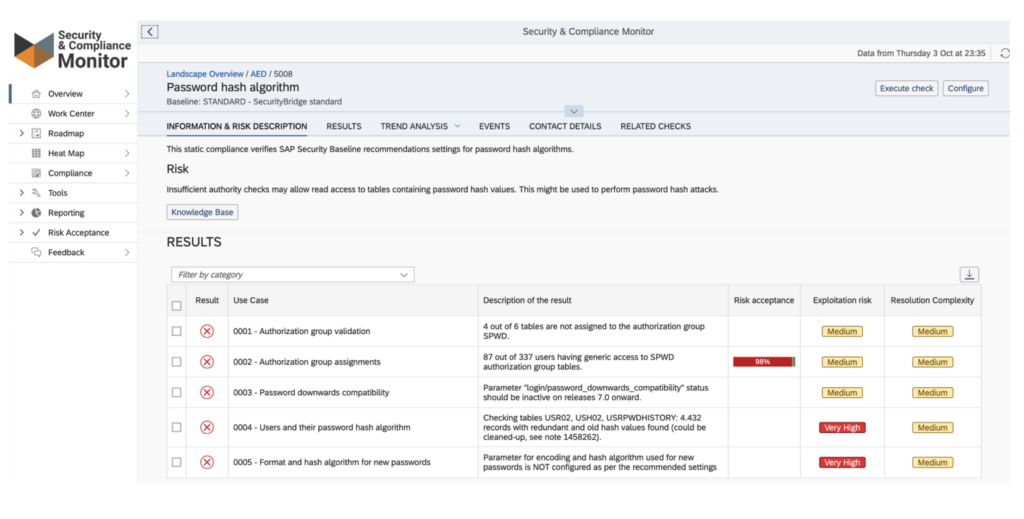
It’s been a personal mission for a long time to try to make the world a bit more secure, and seeing this growing traction is very fulfilling and rewarding.
But we’re definitely not there yet. There are so many developments happening in parallel within the SAP ecosystem, from cloud migrations to the end of support for SAP ECC in 2027, to all the AI developments, the introduction of SaaS solutions, and other impactful changes. These developments sometimes compete for resources and budget to work on SAP cybersecurity initiatives. However, we are increasingly seeing customers understand and acknowledge the importance of climbing up the SAP cybersecurity maturity ladder.
Conclusion
Since writing the above-mentioned blog 10 years ago, SAP customers have increasingly focused on SAP Cybersecurity, with much more awareness of the topic. This progress is encouraging from the defenders’ perspective and is necessary in modern times to ensure that business-critical applications continue running securely.
The SecurityBridge platform supports SAP customers by providing insights into various SAP cybersecurity aspects, including Threat Detection, Vulnerability Management, Code Security, and more.
Are you interested in learning more? We’d be happy to share about the unique capabilities of the SecurityBridge Platform. For more SAP security-related news, articles, and whitepapers, be sure to follow us on LinkedIn and other social media platforms!

