
Preventing unauthorized access and data loss in SAP
Chapters
Share Article
Let's Talk SAP Security
Have questions about SAP Security? We’re here to help. Contact Us
Executive Summary
Defense, aerospace, and pharma organizations manage some of the world’s most sensitive digital assets – restricted technical data, maintenance procedures, engineering drawings, supply chain specifications, and classified-adjacent operational information.
In modern ERP-centric operations, this data primarily lives inside SAP.
Traditional cybersecurity tools focus on network perimeters and endpoint protection.
However, most real data exposure incidents in regulated environments originate inside the business application layer:
- Authorized users exporting more data than intended
- Privileged users accessing restricted programs
- Forgotten interfaces extracting data automatically
- External attackers abusing trusted SAP connectivity
- Insufficient controls for export-controlled information (ITAR / national regulations)
SecurityBridge provides application-native Data Loss Prevention (DLP) and access protection directly inside SAP, combining detection and preventative enforcement aligned with Zero-Trust principles.
The Regulatory & Threat Reality
Defense organizations must simultaneously satisfy multiple requirements:
- Export control regulations (e.g., ITAR-like frameworks, national export laws)
- Protection of restricted technical data
- Protection of the supply chain and logistics processes
- Operational continuity of critical infrastructure
- Auditability (GDPR) and accountability of privileged users
- Demonstrable enforcement – not only monitoring
At the same time, the threat landscape has evolved:
Threat Type
Typical SAP Impact
Insider risk
Mass extraction of engineering or logistics data
Privilege misuse
Unauthorized viewing of restricted material
Supply-chain compromise
Interfaces (RFC) used as hidden extraction channels
Nation-state activity
Long-term data exfiltration via trusted protocols
Audit failure
Lack of preventive controls around sensitive tables
Most incidents do not exploit SAP vulnerabilities; they exploit legitimate functionality without proper contextual control.
The SecurityBridge Approach: Prevent + Detect
SecurityBridge implements layered controls directly within SAP operations:
1) Detective Controls – Continuous visibility and an early warning system
2) Preventive Controls – Real-time enforcement before exposure via risk-aware MFA
This dual model enables both operational monitoring and regulatory compliance.
1. Detective Controls – Continuous Visibility
Detective controls provide full transparency across user behavior and system communications without interrupting operations.
Download Monitoring (Non-Blocking DLP)
SecurityBridge monitors all data extraction activities – not only critical tables, any download.
Capabilities
- Detect downloads from reports, tables, transactions, and files
- Identify multi-table and critical data extractions
- Track extraction by user, terminal, environment, and timestamp
- Notify users and compliance teams in real time
- Provide contextual compliance warnings
Security Value
- Creates security awareness and deterrence
- Enables early intervention
- Provides audit-grade logging
Clipboard Data Capture
Sensitive information is often copied to the clipboard rather than exported.
SecurityBridge detects:
- Copy-paste of (sensitive) SAP data
- Attempted manual extraction workflows
- Non-file-based exfiltration behavior
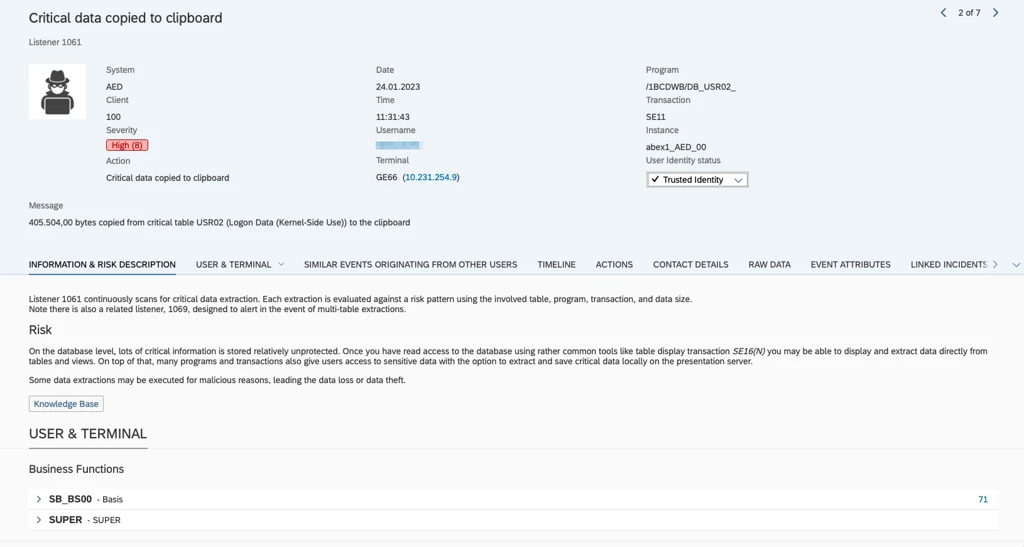
Example: Critical data copied to clipboard
Privileged User Extraction Monitoring
Superusers are the highest-impact risk category.
SecurityBridge tracks:
- Administrative data exports
- Privileged table access
- Unusual data volume behavior
- After-hours abnormal, sensitive activity
This provides the accountability required in regulated environments.
Interface Traffic Monitoring (Detection Mode)
The platform continuously analyzes SAP communications:
- Abnormal RFC usage
- Unexpected system-to-system communication
- External endpoint activity
- High-volume extraction patterns
- Lateral movement indicators
Security teams gain a clear picture of how data leaves SAP, not only who accessed it.
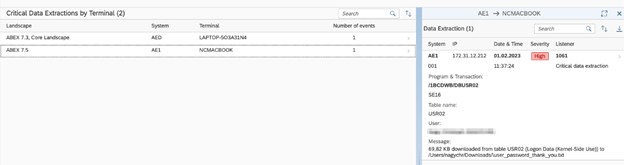
Critical data exfiltration overview
2. Preventative Controls – Real-Time Protection
In defense environments, monitoring alone is insufficient. Regulations increasingly require active enforcement. SecurityBridge introduces preventive controls embedded directly within SAP processes.
Context-Based Policy MFA (Zero-Trust Inside SAP)
SecurityBridge enforces authentication at the moment of risk – not only at login. This MFA happens AFTER the user is already logged into SAP, and will require a second, context-based MFA whenever risky activities are about to be performed (Step-up authentication).
Trigger examples
- Accessing export-controlled tables
- Running sensitive reports
- Executing mass extraction
- Privileged configuration access
Policy context
- User role
- System environment
- Risk level of activity
- Organizational policy attributes
This creates a powerful Zero-Trust operational model within SAP. Authorization is continuously verified rather than assumed. These kinds of controls are becoming mandatory in the defense, export-controlled, and critical infrastructure industries (such as Opérateur d’Importance Vitale (OIV) in France).
Blocking Risky Downloads
SecurityBridge can actively block sensitive downloads. Users get a contextual warning message explaining why their download was blocked. Additionally, alerts can be sent to the appropriate compliance department for further investigation if desired.
What downloads can be blocked
- Critical tables
- Export-controlled datasets
- Restricted engineering information
- High-volume downloads
- Unauthorized report execution
Blocking RFC and Interface-Based Data Leakage
Interfaces are a primary extraction vector because they operate silently and automatically.
SecurityBridge prevents leakage by:
- Identifying abnormal or unauthorized data flows (such as high-volume RFC calls)
- Detecting unusual communication endpoints and unexpected system-to-system traffic
- Blocking suspicious connections
- Disabling obsolete or insecure interfaces
- Reducing lateral movement risks
This removes hidden extraction channels often missed by SIEM or network tools.
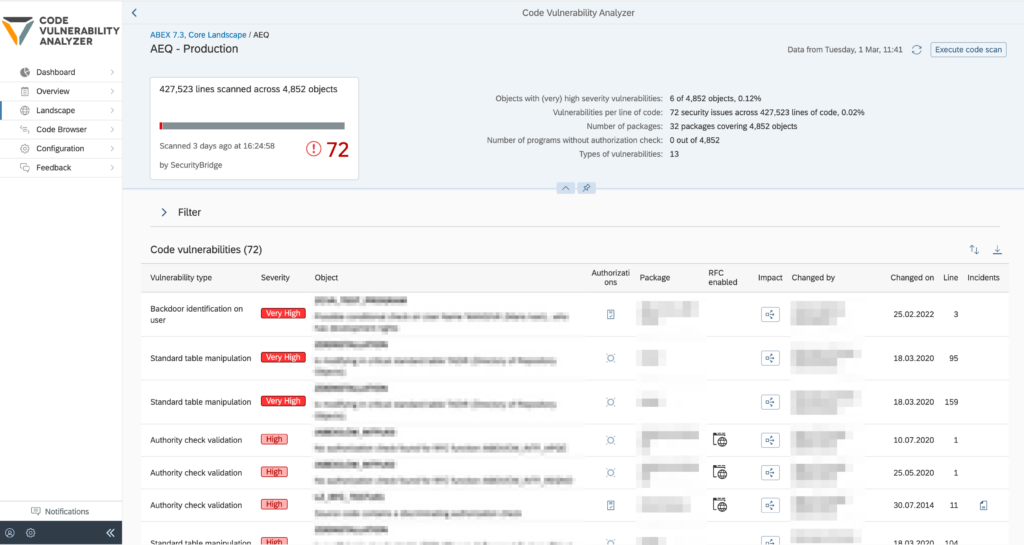
Securing Custom ABAP Code
Custom developments frequently bypass governance controls.
SecurityBridge identifies:
- Hardcoded extraction logic
- Unauthorized table reads
- Missing authorization checks
- Embedded export functionality
This closes a major compliance gap: data leakage through business logic rather than user actions.
Why Application-Layer DLP Matters
Traditional DLP tools operate outside SAP and cannot understand its business context.
Traditional Security
SAP-Native SecurityBridge
Sees files
Sees business data meaning
Detects after export
Stops extraction at source
No transaction context
Full user & process context
Network-based
Application-embedded
Reactive
Preventative
Operational Impact & Conclusion
Protecting sensitive SAP data requires more than monitoring activity after exposure; it also requires enforcing controls when the risk arises.
By embedding Data Loss Prevention directly within SAP processes, SecurityBridge enables organizations to prevent unauthorized access to and extraction of restricted information.
Organizations achieve:
- Reduced insider risk exposure
- Enforceable export-control and compliance protection
- Controlled privileged access to sensitive data
- Elimination of hidden extraction paths through interfaces
- Audit-ready monitoring and traceability
- Faster investigation and incident response
- Alignment with Zero-Trust security principles
Instead of relying on perimeter tools or post-event detection, SecurityBridge protects sensitive business data where it resides – inside operational workflows.
The result is not only visibility into potential data exposure, but real-time prevention and demonstrable control over critical information.
