
What's the Difference: SAP Patch Management vs. Vulnerability Management

Chapters
Share Article
Believe it or not, I’ve probably attended more customer meetings in 2022 than ever before. And the question about the difference between SAP Patch Management and SAP Vulnerability Management keeps appearing. To give a conclusively answer, we need to take a closer look at the two separate areas.
SAP patching is strongly underestimated
When SAP customers want to increase system security, they often ask: “Where do I start?” If you have not already done so, we recommend installing the missing SAP Security Fixes. To accomplish this requires some preparation and even follow-up. Here is a brief overview of the manual preparation work, should you not have an efficient solution such as SecurityBridge Patch Management in place:
- Analyze the SAP components and software versions in use.
- Retrieving the available security patches and filtering the relevant corrections.
- Definition of an installation strategy (e.g., in the context of a development release).
- Reading all corrections and checking manual rework.
- Implementation of the patches in the development system.
- Software deployment into the test environment
- Acceptance in the context of a user acceptance test
- Cutover into the production environments.
The above list may differ slightly in individual cases, but it mostly corresponds to what is meant by SAP Patch Management.
Key Differences
Back to the initial question: What is the difference between Vulnerability Management and Patch Management?
There are many types of vulnerabilities an SAP customer must deal with. A look at the SAP Secure Operation Model helps to delineate the areas of concern. This is divided into five different levels:
- Environment
- System
- Application
- Process and
- Organization
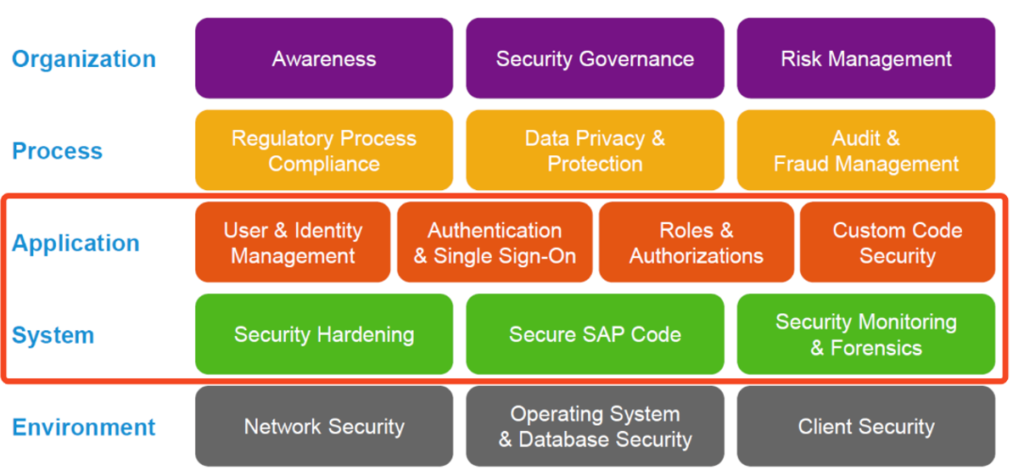
To further narrow down the target corridor of SAP Vulnerability Management, we focus on application security, meaning the levels of Application and System.
In conclusion, we can state that you can achieve comprehensive and holistic SAP Vulnerability Management with:
- User & Identity Management
- Authentication
- Roles & Authorization
- Custom Code Security, but also
- Security Hardening and
- Secure SAP Code
The latter should attract your attention. From the customer’s point of view, the term “Secure SAP Code” can only mean the prompt installation of security corrections provided by the manufacturer.
Conclusion
Patch Management for SAP is a variety of activities that deal with organizing and planning patch activities of business-critical SAP applications. At the same time, patching and monitoring missing patches are part of the overall SAP Application Vulnerability Management process.
