
SAP Cloud Connector

Chapters
Share Article
Every organization constantly faces the challenge of minimizing the attack surface that an adversary could use to perform malicious operations. To do this, administrators must install the deployed components and understand them in detail to identify risks and proactively mitigate or prevent those. Today we are looking at what is necessary to protect the SAP Cloud Connector.
What is the SAP Cloud Connector?
When installing and operating the SCC, administrators need to consider several things to ensure security. A good starting point is the manufactures SAP Cloud Connector Security Guidelines, which include the topics:
- Network zones concept
- Administration UI
- High Availability
- On-Premise Configuration
- Audit Logging
- OS-Level Protection
- Protocol Security and
- Instances.
A new and remarkable feature of the SAP Cloud Connector is that it has an integrated security check, which provides the administrator with information about the existing issues. Not only is there a kind of checklist, but it displays a status that shows which problem currently exists. How to find the feature? Find it from the Connector menu and choose Security Status to access an overview showing potential security risks and the recommended actions.
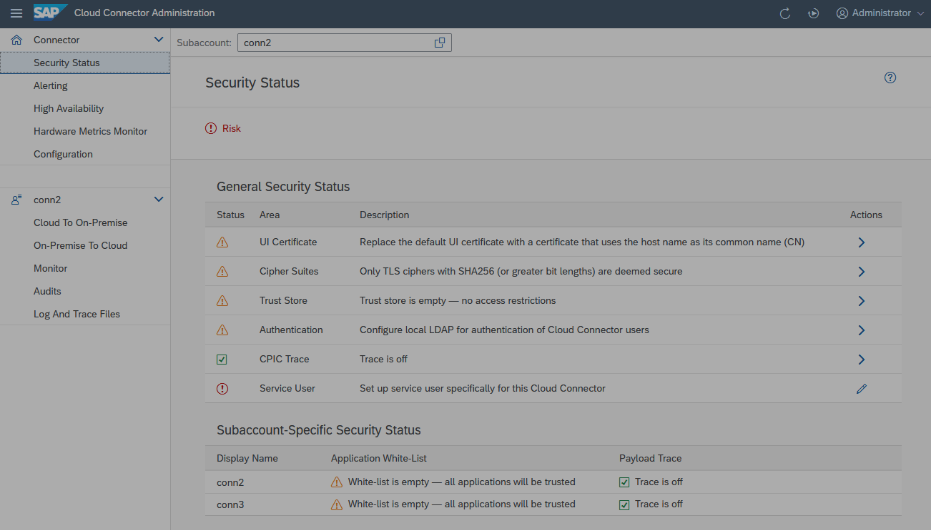
The SCC distinguishes between general and sub-account-specific problems. In the General Security Status area, customers will find general issues. In the lower area, you will then see the sub-account issues.
Problem 1: Often, these recommendations have not been implemented or are only partially implemented.
Often, technical components are installed and then forgotten if they perform their service and do not break anything that works. To make matters worse, these components usually are provided by external service providers. As a result, there is not enough internal expertise available within the company for regular security checks or the remediation of security problems.
Problem #2: The SAP Cloud Connector isn’t integrated enough into the lifecycle management of the SAP operation. This neglect can lead to security problems that are not detected or resolved in time.
SAP releases regular enhancements for all products in the software’s portfolio. It is the customer’s responsibility to check on-premise components for security vulnerabilities for which a patch has been provided and to close this loophole on time. In addition, you must include other software products used by SAP SCC in the equation. Examples are the Java Virtual Machine (JVM) version and the Tomcat web server.
Problem #3: Also, due to the lack of integration into the software lifecycle management, customers aren’t aware of security patch releases and don’t implement them or aren’t fast enough. You can find the available SAP Security Patches for the technical component on the SAP Support Portal using the following query: Display security patches for SAP Cloud Connector.
SAP products are usually extensive in their logging. This makes it possible to track circumstances and situations occurring during regular operations. However, the number and variety of security logs poses a challenge for many customers. If they’re enabled, they are usually only used by the administrator for error analysis and troubleshooting. Few manage to transfer this valuable information to the Security Operation Center (SOC), and only very few apply valuable use cases making real use of the collected data.
Problem #4: Security logs are not enabled or monitored. There is no concept for alerting when an anomaly occurs, and thus attack actions such as exploiting vulnerabilities are not detected.
The SAP Cloud Connector builds a bridge to the outside world. Communication with public networks is dangerous because external attackers can intercept and analyze data packets. Therefore, protocol security and network architecture are important. At this point, we want to motivate our readers to support the Feature Request “Implement SNC support for incoming RFC in SAP Cloud Connector” In the SAP Customer Influence Portal.
Problem #5: The system architecture isn’t optimized. For example, the SAP Cloud Connector in the DMZ shares a host system with other components. Alternatively, the protocol security isn’t guaranteed so attackers can intercept, redirect, or manipulate the packets.
Addition:
Based on our field service’s reports, we found SAP Cloud Connector installations in production environments that used the portable version. For productive use, SAP strongly recommends using the installer version.
Conclusion
The integration of technical components such as the SAP Cloud Connector or the SAP WebDispatcher into the in-house software lifecycle management processes requires special efforts from the customer. To achieve a resilient posture against cyber-attacks, both the hardening of software components and monitoring of whether the measures are working must be carried out.
Security updates must be identified and implemented on time, and security logs must be monitored continuously for suspicious activity to detect attacks as they occur.
You may think this is a massive hurdle until you experience solutions like the SecurityBridge Platform for SAP. SecurityBridge provides a holistic cyber-security coverage addressing the need of SAP customers directly from within your SAP landscape.
