
HOW TO SECURE SAP INTERNET COMMUNICATION MANAGER (ICM)?

Chapters
Share Article
Let's Talk SAP Security
Have questions about SAP Security? We’re here to help. Contact Us
In ancient times it was very rare having SAP systems exposed to the internet. Due to technical challenges and different use-cases, the SAP application servers resided in the shielded environment of the hosting center, often directly at customer premises. Giant air conditioners were required to cool the servers, as they had to provide services to the employees sitting behind their desktop PCs. A lot has changed since then, and the global pandemic has even lifted the need for exposed web-bases services provided by the SAP ICM that are available on the go, and from home offices, but can also be consumed via smartphones and tablets. With this change of paradigm, the security aspect for sensitive data residing in the SAP application needs to be rethought.
What is SAP ICM?
Anticipated by the name, the SAP Internet Communication Manager ensures that communication between the SAP System (NetWeaver Application Server) and the outside world via HTTP, HTTPS, and SMTP protocols works properly. In other words, once activated in transaction SMICM, the SAP NetWeaver Application Server provides a web server that serves as the foundation for web-based SAP technologies like Fiori, WebDynpro, or Business Server Pages (BSP).
The ICM comes with many security-relevant configurations for SSL encryption, cookie handling, authentication requests (HTTP) and even provides a dedicated security log. Tools like SecurityBridge Security & Compliance Management assesses the secure configuration of the ICM in SAP NW and provides guidance for customers to harden the webserver.
Network Segmentation and Service Decoupling
SAP provides various concepts to decouple the business-critical application from the systems providing services to untrusted networks. The SAP Gateway for example may be sitting in the DMZ, which allows exposing various OData services to the outside. For web-based access, the SAP Web Dispatcher provides a solution. The technology shift from remote function call more towards HTTP is mainly driven by the demand for open infrastructure and accessibility of services. Network segmentation and service decoupling is vital step towards increasing the security posture.
Secure the SAP Internet Communication Manager
While it never was a good practice to have too many services being enabled – it becomes a security nightmare in scenarios where connections to untrusted networks exist. In our recent article “Understand and Reduce the Attack Surface” we describe how SAP customers need to gain control and actively manage their security posture with the ultimate goal to reduce whatever is not needed from a business perspective.
Sticking with the Internet Communication Manager, which exists as a separate process within SAP NetWeaver Application Servers, it is possible to use system profile parameters to define whether the ICM is to be started and how it is to be configured. SAP’s Security Baseline template provides additional recommendations to prevent unintended Information Disclosure, for example by securing public endpoints that do not require authentication.
Depending on the customer-specific scenario,
server port number (profile parameter icm/server_port_<num>) and
HTTP admin port (profile parameter icm/HTTP/admin_<num>) shall be adjusted. Both ports should be protected by SSL over HTTP.
Enable and configure the ICM Security Log logging
A dedicated ICM Security Log is available for the Internet Communication Manager of SAP NW Application Server and the SAP Web Dispatcher. In newer SAP versions, the log is active by default and can be further tuned by profile parameter “icm/security_log”. The recommended settings according to the security setting of S/4HANA can be found in note 2926224.
Example from SAP Security Baseline Template v2.3:
icm/security_log= LOGFILE=dev_icm_sec_%y_%m,LEVEL=3,MAXFILES=2,MAXSIZEKB=50000,SWITCH TF=month
SecurityBridge customers have a dedicated control for this via the Security & Compliance Management application. For details refer to check U5037-0012, “Configuration of ICM Security Log”, which also provides guidance to securely configure your ICM using our best practice settings.
Concerns about performance can be neglected since this is not measurable. Only security-relevant entries are stored in this log. The entries are then, for example, of the type “Content filter matched: Permission denied” if a URL filter was applied. Or “NULL bytes in HTTP request”, which is also an indication of HTTPS traffic on the HTTP port.
It is recommended to copy the log data to another system to have it available for later forensic investigations after an intrusion. This is because an attacker may try to cover his tracks by manipulating or deleting the files. Correlation with other log sources is also easier to perform on specialized systems than in the file system or SAP NetWeaver.
Patch SAP ICM Vulnerabilities
While the SAP Web Dispatcher provides dispatching and performance load balancing capabilities, it shares the same code basis with the SAP ICM. This means that both components may share the same vulnerabilities.
Worthless to emphasizing – It is not a good practice to only rely on the security patches, but having no process in place, that ensures timely installation of issued correction e.g. via the SAP Security Patch Day, can lead to a security disaster. SAP customers need to sift through their installed base, to identify components that need to be patched, this is particularly important for components like the SAP Internet Communication Manager (ICM) that expose services to untrusted networks like the internet.
On February 8, 2022, three vulnerabilities one of them with CVSS 10.0 in SAP Internet Communication Manager (ICM) and SAP Web Dispatcher were fixed as part of SAP Security Patch Day of February 2022. Affected customers should apply the SAP security patches immediately or use the available workaround.
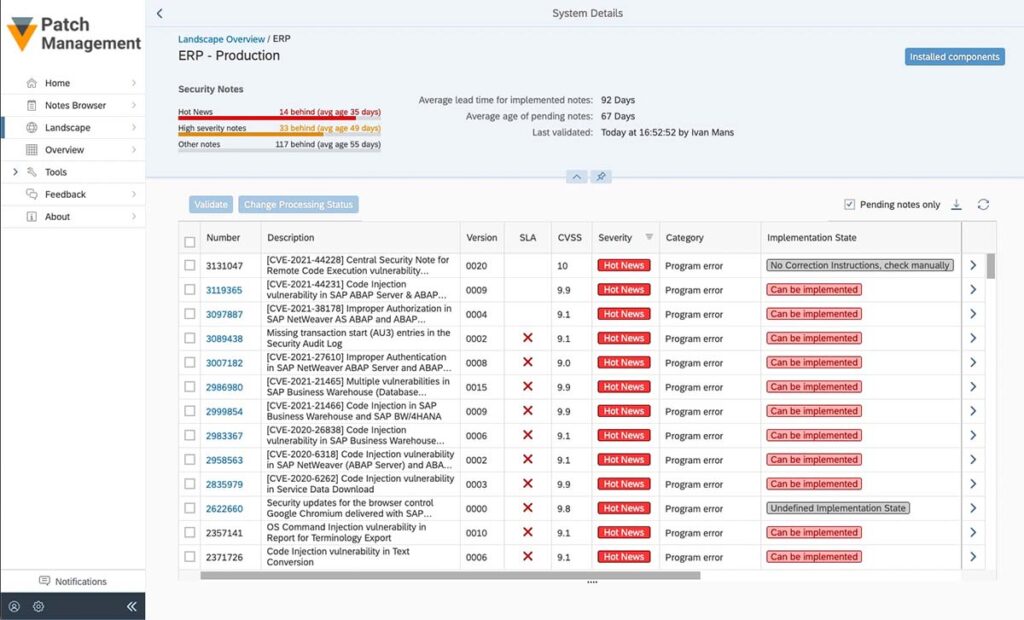
Above you can see an example from SecurityBridge Patch Management that provides an overview of missing SAP Security patches.
We recommend that SAP customers – irrespective of the use of an SAP Cybersecurity solution – obtain an overview of missing security updates and install them promptly if possible and in coordination with the necessary departments.
If the installation of a critical fix like “3123396 – [CVE-2022-22536] Request smuggling and request concatenation in SAP NetWeaver, SAP Content Server, and SAP Web Dispatcher” is not possible, please check if a workaround exists to mitigate the risk.
