
SAP Cloud Security for Robust Data Protection
Optimizing SAP Cloud Security for Robust Data Protection
SAP Cloud Security is crucial for safeguarding business data in the face of increasing cyber threats. This article covers essential measures for securing SAP cloud environments, such as compliance, encryption, access controls, and monitoring solutions. SAP cloud security is a subcomponent of general SAP Security.
Key Takeaways
SAP Cloud Security integrates encryption, compliance with industry standards, and monitoring solutions to protect critical data.
The shared responsibility model highlights the distinct roles of service providers and customers in securing cloud environments for SAP solutions.
Enhanced SAP security measures, including multi-factor authentication (MFA) and regular audits, are essential for safeguarding SAP systems against cyber threats.
Understanding SAP Cloud Security
SAP Cloud Security refers to various measures to protect business-critical data in SAP systems. It combines software solutions and proactive strategies that extend beyond built-in SAP security features. Cloud security refers to the need for customers to integrate their systems within the organizational network to prevent SAP security gaps.
Recognizing the significance of complying with regulations, encryption, data protection, and effective monitoring solutions for threat detection is crucial in SAP Cloud Security. These elements are fundamental to maintaining a robust security posture for your SAP solutions, which are often used for business-critical operations such as enterprise resource planning (ERP), business intelligence, supply chain management, Human Resources, etc.
Compliance with Industry Standards
Adherence to industry standards, such as ISO 27001, SOC 2, and PCI DSS, is a cornerstone of SAP Cloud Security, ensuring secure data management and security requirements.
Additionally, SAP provides tools like SAP GRC to help organizations manage compliance with various regulations, including GDPR and SoX, ensuring high data-safeguarding standards.
Encryption and Data Protection
Encryption and data protection play vital roles in cloud security. Cloud security uses encryption to protect sensitive data and incorporates monitoring solutions and access controls for enhanced protection. Multi-layered data security strategies help safeguard SAP cloud environments from unauthorized access and breaches.
These measures ensure adherence to privacy regulations and protect sensitive data from unauthorized access.
Monitoring Solutions and Threat Detection
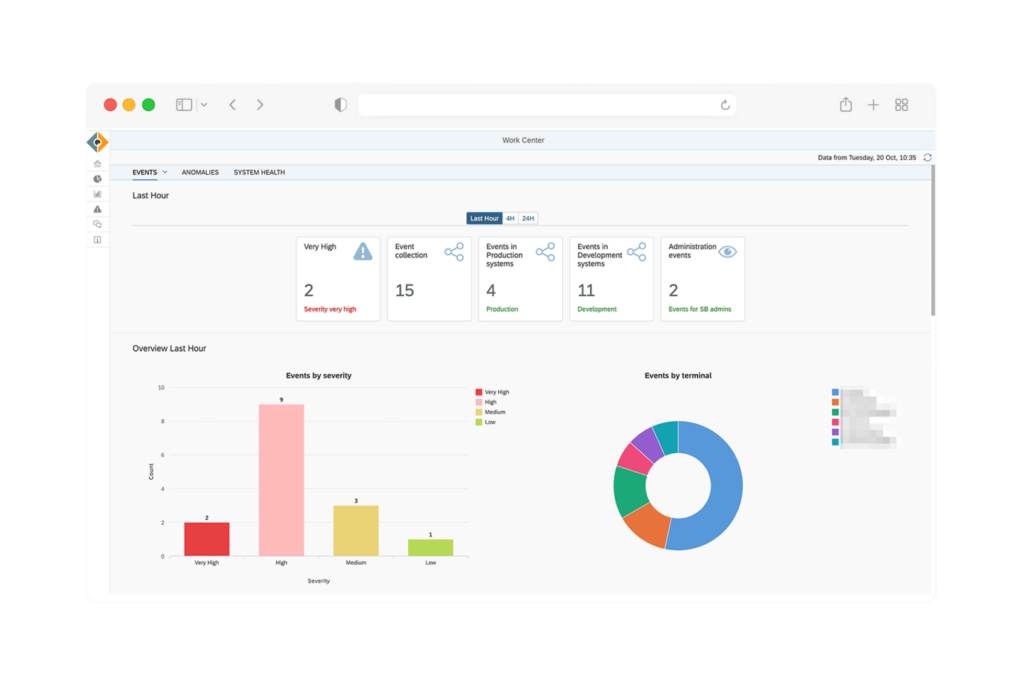
Monitoring solutions are essential in protecting SAP cloud solutions. Platforms like SecurityBridge analyze human and machine-to-machine communication within SAP applications, offering insights into security vulnerabilities. Security monitoring solutions enhance data protection and help maintain compliance, enabling organizations to identify and address potential cyber threats promptly.
Key Differences Between Cloud and On-Premise Security
Grasping the key differences between cloud and on-premise security is vital for implementing effective measures. Cloud security protects systems hosted on the cloud and managed by service providers, while the customer directly controls on-premises security.
This distinction impacts how security controls are implemented and managed.
Shared Responsibility Model
The shared responsibility model clarifies the security obligations of the cloud system service provider and the customer. The provider secures the infrastructure, while the customer is responsible for their data and applications. This model ensures clear role definitions for maintaining a secured cloud environment.
Role-Based Access Controls
Role-based access controls (RBAC) are vital in cloud solutions and on-premise environments to ensure users have only the permissions necessary for their roles. Monitoring and managing user permissions enhances transparency and helps mitigate insider threats.
Regular audits and access reviews are vital for ensuring access controls remain effective.
Enhancing SAP Cloud Security Measures
Enhancing cloud security measures is crucial to protecting against cyber-attacks and internal risks. A combination of MFA, regular security audits, and continuous employee training can significantly improve the security posture of cloud systems.
Multi-Factor Authentication (MFA)
Multi-factor authentication (MFA) reduces the risk of unauthorized access by requiring multiple verification forms. Implementing MFA adds a layer of security, making it much harder for unauthorized users to access SAP systems.
Regular Security Audits
Regular security audits are vital for maintaining a strong security posture in SAP cloud solutions. They help identify potential vulnerabilities, ensure adherence to security protocols, and prepare organizations for potential security incidents that could impact their infrastructure.
Employee Training and Awareness
Continuous employee training and awareness programs can reduce human-related security risks in SAP environments. These programs educate employees about security risks and best practices, thereby minimizing human error.
SAP Identity Management for Secure Cloud Operations
SAP Identity Management is crucial for managing user lifecycles and integrating identity and access management within business processes. It ensures secure access and simplifies user provisioning, enhancing overall security in SAP cloud operations.
Integration with Business Processes
SAP Identity Management streamlines user provisioning by automating identity lifecycle processes and integrating with existing corporate identity providers. This seamless integration is vital for access management within various business processes.
Centralized User Access Management
Centralized user access management enhances security by providing centralized control of user access across different business environments. However, it does not manage segregation of duties, which can pose risks and require additional controls.
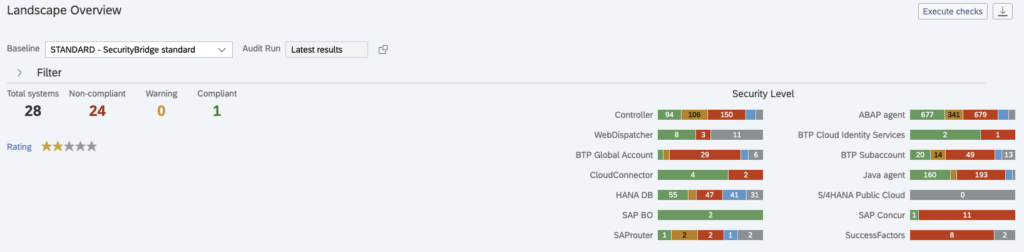
Ensuring Compliance in SAP Cloud Systems
Regulatory adherence is crucial for organizations using SAP cloud solutions. It enables businesses to meet various regulatory requirements effectively, including GDPR and SoX.
Compliance Management Tools
Automated auditing and continuous control monitoring are practical tools for managing compliance. Tools like SAP GRC and SAP Process Control help organizations monitor and manage different regulatory frameworks. Platforms such as SecurityBridge automate the process even further and centralize it into a single UI.
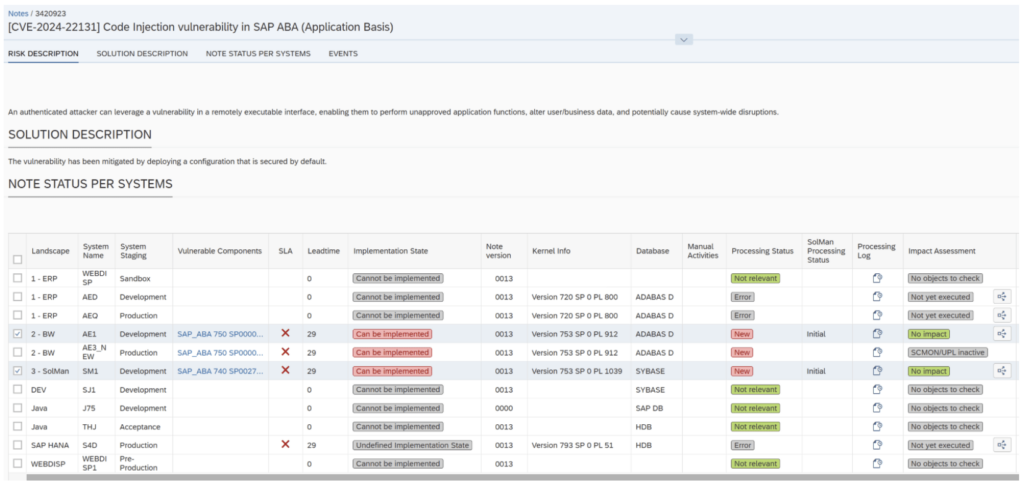
Data Encryption and Privacy
Data encryption and privacy are essential for protecting sensitive information and ensuring compliance. SAP HANA uses AES 256-bit encryption for data and log backups and securely hashes passwords with PBKDF2.
SAP manages encryption keys, ensuring robust privacy controls.
Protecting Against Common Threats in SAP Cloud
Robust security measures are needed to protect SAP cloud systems against common cyber risks. Robust access controls and continuous security monitoring can mitigate unauthorized access and data breach risks.
Insider Threats
Insider threats can arise from employees or contractors misusing their access to sensitive data intentionally or unintentionally. Detecting these security incidents is challenging due to the complexity of effectively monitoring suspicious activity and changes in access logs.
Data Breaches and Incident Response
A well-defined incident response plan is crucial for promptly addressing data breaches in SAP environments. Quick identification and response can significantly reduce the impact of a cyberattack on SAP customers’ businesses.
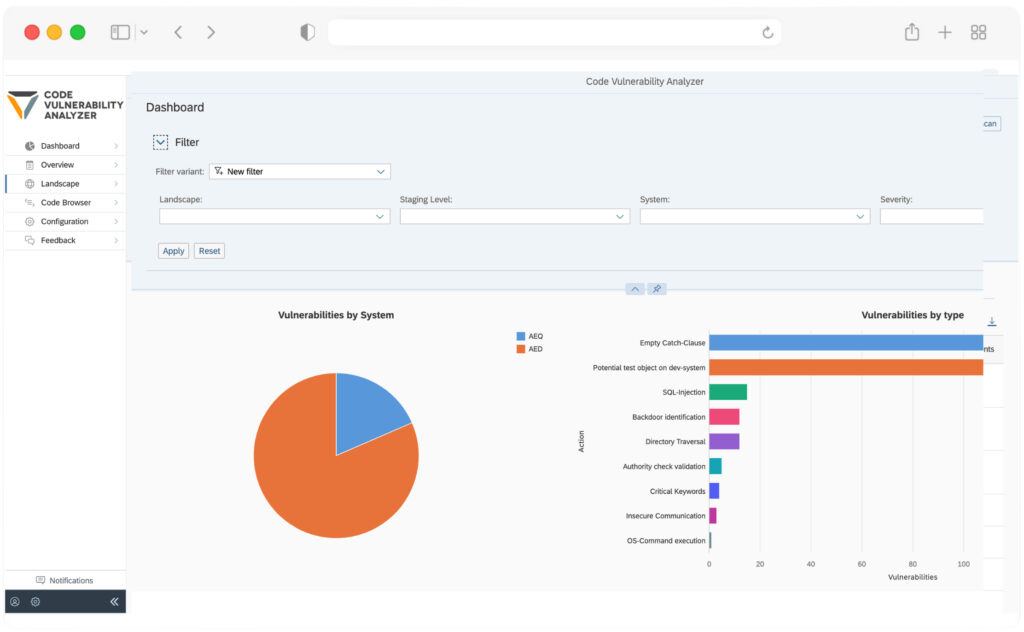
Best Practices for Secure Programming in SAP Cloud
Secure programming practices are vital for maintaining robust security in SAP cloud environments. Integrating security throughout the development process helps identify and address vulnerabilities early.
Secure Development Lifecycle (SDL)
A secure development lifecycle (SDL) for SAP products is mandatory for both on-premise and cloud products. Conducting security risk assessments and threat modeling during the design phase helps identify and mitigate security risks.
Code Review and Testing
Regular code reviews and security testing are crucial for identifying vulnerabilities early in development. Thorough testing ensures strong security measures are in place before code deployment.
Summary
In conclusion, optimizing SAP Cloud Security involves understanding the unique aspects of cloud security, implementing robust security measures, ensuring compliance, and following best practices for secure programming. Organizations can protect their business-critical data and maintain a secure cloud environment by taking these steps.
Frequently Asked Questions
What is the purpose of SAP Cloud Security?
The primary purpose of SAP Cloud Security is to protect business-critical data in the cloud from hackers and data breaches. It ensures the integrity and confidentiality of sensitive information.
What security standards does SAP Cloud Security comply with?
SAP Cloud Security complies with prominent security standards such as ISO 27001, SOC 2, and PCI DSS, ensuring robust protection of sensitive data. This compliance reflects SAP’s commitment to maintaining security measures for its cloud services.
How does SAP Cloud Security protect data?
SAP Cloud Security safeguards data by integrating encryption, robust monitoring tools, and stringent access controls, ensuring comprehensive protection against unauthorized access and data breaches.
What is the difference between SAP Cloud Security and on-premise security?
The key difference lies in their deployment environments: on-premise security safeguards systems hosted locally, whereas cloud security specifically protects cloud-based SAP systems. This distinction is crucial for organizations when determining their security strategies.
What does SecurityBridge Threat Detection analyze?
SecurityBridge Threat Detection analyzes all human activity and machine-to-machine communication within an SAP application, ensuring a comprehensive evaluation of security threats. This analysis is crucial for maintaining the integrity of SAP systems.
