
The Complete SAP Security Assessment Checklist to Improve the Cybersecurity Posture
Chapters
Share Article
Let's Talk SAP Security
Have questions about SAP Security? We’re here to help. Contact Us
In this blog, you’ll find a detailed SAP security assessment checklist including what to look out for such as roles, transaction monitoring, vulnerability management, and what is needed on a high level to adhere to various cybersecurity frameworks.
Key Takeaways
Regular SAP security assessments are essential for identifying vulnerabilities and ensuring adherence to regulatory requirements.
Key components of SAP security assessments include reviewing roles and authorizations, transaction monitoring, vulnerability management, and patch management.
Understanding SAP Security Assessments
Implementing SAP security assessments aims to protect sensitive information from unauthorized access and potential cyber threats. They identify vulnerabilities, ensure compliance with data protection regulations, and strengthen system resilience.
Regular assessments can significantly reduce the risk of incidents that could harm a company’s reputation.
A thorough SAP security assessment links to a cybersecurity framework and includes:
Roles
Transaction monitoring
Vulnerability management
Transport security
These maintain data and database security and protect critical assets. Frequent assessments help organizations identify complex security operations gaps, implement necessary measures effectively, and compare them against whatever they have chosen to be the best cybersecurity framework.
Key Components of SAP Security Assessments
SAP security assessments cover roles, authorizations, transaction monitoring, and vulnerability management.
Understanding these individual components is crucial for effectively protecting SAP systems and, for example, passing an SAP security audit.
Roles and Authorizations Review
User Access Reviews validate whether permissions remain relevant over time, especially after job function changes. Reviewing roles and authorizations maintains proper access controls to the SAP system, preventing unauthorized parties from gaining access to, for example, customer data.
SAP components like GRC streamline the reviews by presenting complex role information easily. They also identify discrepancies in user permissions, ensuring only authorized personnel can access critical assets.
Transaction Monitoring
Transaction monitoring in SAP systems identifies unusual activities that could indicate potential breaches affecting business processes. Continuous monitoring of transaction usage and remote access identifies unauthorized activities and ensures adherence to company policies and cybersecurity frameworks.
Transaction monitoring scrutinizes transaction performance and detects anomalies indicating a breach. This proactive approach enables the timely detection of vulnerabilities, essential for adapting to evolving cyber threats and following cybersecurity frameworks.
Vulnerability and Patch Management
Continuous patch management addresses known vulnerabilities and protects against evolving threats in a SAP system. Timely application of security patches maintains SAP systems’ protection, integrity, and reliability.
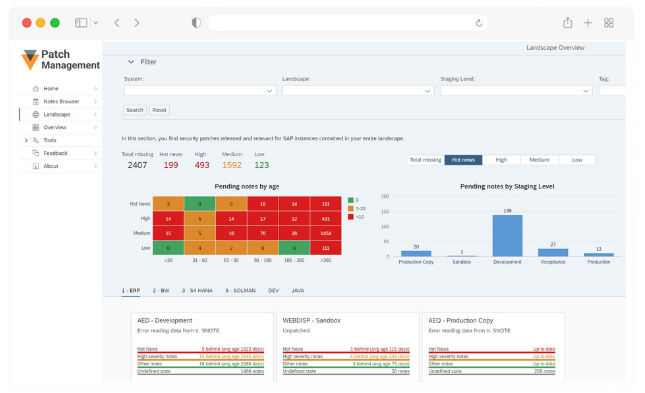
SecurityBridge Patch Management
Custom Code Security
Reviewing custom ABAP code ensures it does not contain flaws exploitable for cyber attacks. Regular evaluation of custom ABAP code identifies flaws that could expose systems such as the SAP HANA Cloud to threats.
The SecurityBridge Code Vulnerability Analyzer (CVA) identifies and rectifies security flaws in ABAP code before deployment. Available on the cloud through SAP Business Technology Platform (BTP) and as an on-premise solution, CVA ensures custom code is secure.
Transport Security
Securing transport routes in SAP protects data during transfer across different environments and SAP components. Implement measures like firewalls and SAP routers to secure transport routes in SAP.
Use secure network devices to safeguard SAP transport pathways from unauthorized access. Measures should include monitoring and controlling data exchanges to protect sensitive configurations.
Compliance Testing in SAP Security
Testing verifies that SAP systems adhere to industry-specific regulations and standards (such as the NIST cybersecurity framework, also known as the NIST CSF) related to data protection, data integrity, and security configurations.
Tools for SAP Security Testing
SAP security testing identifies weaknesses in SAP systems to prevent breaches and ensure smooth operations. Common solutions for security testing include vulnerability scanners, penetration testing tools, security logging, and code analysis utilities.
Automated solutions in SAP security testing improve efficiency, accuracy, and coverage across the system landscape. These solutions maintain a robust security posture by identifying and mitigating potential threats.
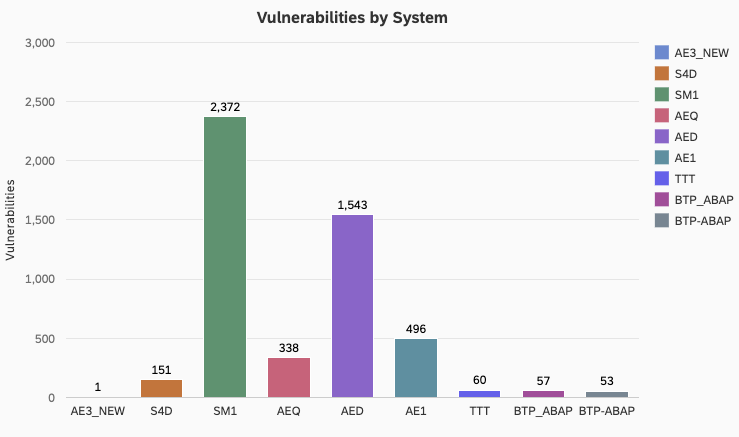
Protecting Data in SAP Systems
A cybersecurity framework also guides the process of ensuring SAP systems meet best practices for data protection and the security requirements associated with it.
Data Encryption
Robust encryption mechanisms safeguard sensitive data (such as intellectual property) in SAP systems to avoid data misuse. Encryption methods in SAP systems secure sensitive data when stored and during transmission. The SAP Cryptographic Library offers a range of encryption options that are supported by SAP. Customer-specific encryption keys protect data at rest, enhancing overall system security.
Network Segregation
Network segregation restricts access to essential assets and minimizes exploitable gaps. By isolating critical systems from less secure zones, it prevents unauthorized access and enhances data security.
Two-Factor Authentication
Two-factor authentication enhances security, particularly for data accessed by remote workers. Organizations can set up two-factor authentication to significantly increase security posture.
Regular Assessments and Updates
Regular assessments of your security practices help maintain the security posture of SAP systems over time. An effective vulnerability management program prevents the exploitation of weaknesses within SAP environments.
Many data breaches are linked to a known vulnerability with available security patches that were not applied. Regular assessments ensure established controls remain effective and adapt to changes in the threat environment to limit the impact of cyber attacks.
Engaging Security Professionals
Hiring experts for SAP security management provides access to specialized knowledge and experience. Managing SAP security is complex due to the nature of the SAP infrastructure and strict security requirements.
However, without a proper tool or cybersecurity framework, it can be expensive for the business. Also, DIY approaches may leave gaps due to a lack of expertise and resources if a platform like SecurityBridge is not in place. Having a tool for security automation in place, like SecurityBridge, is highly recommended to lower the manual workload associated with maintaining a robust security posture.
Summary
In summary, regular SAP security assessments are essential for protecting sensitive information and maintaining system integrity. By understanding and implementing the critical components of an SAP security audit, organizations can significantly reduce the risk of incidents and ensure adherence to industry regulations and a chosen cybersecurity framework.
Taking proactive measures, such as reviewing roles and authorizations, monitoring transactions, managing vulnerabilities, and securing custom code, will help maintain a robust security posture.
Implementing an SAP security platform like SecurityBridge to guide your security initiatives significantly improves security and guides organizations in hardening SAP landscapes one step at a time while limiting manual workloads.
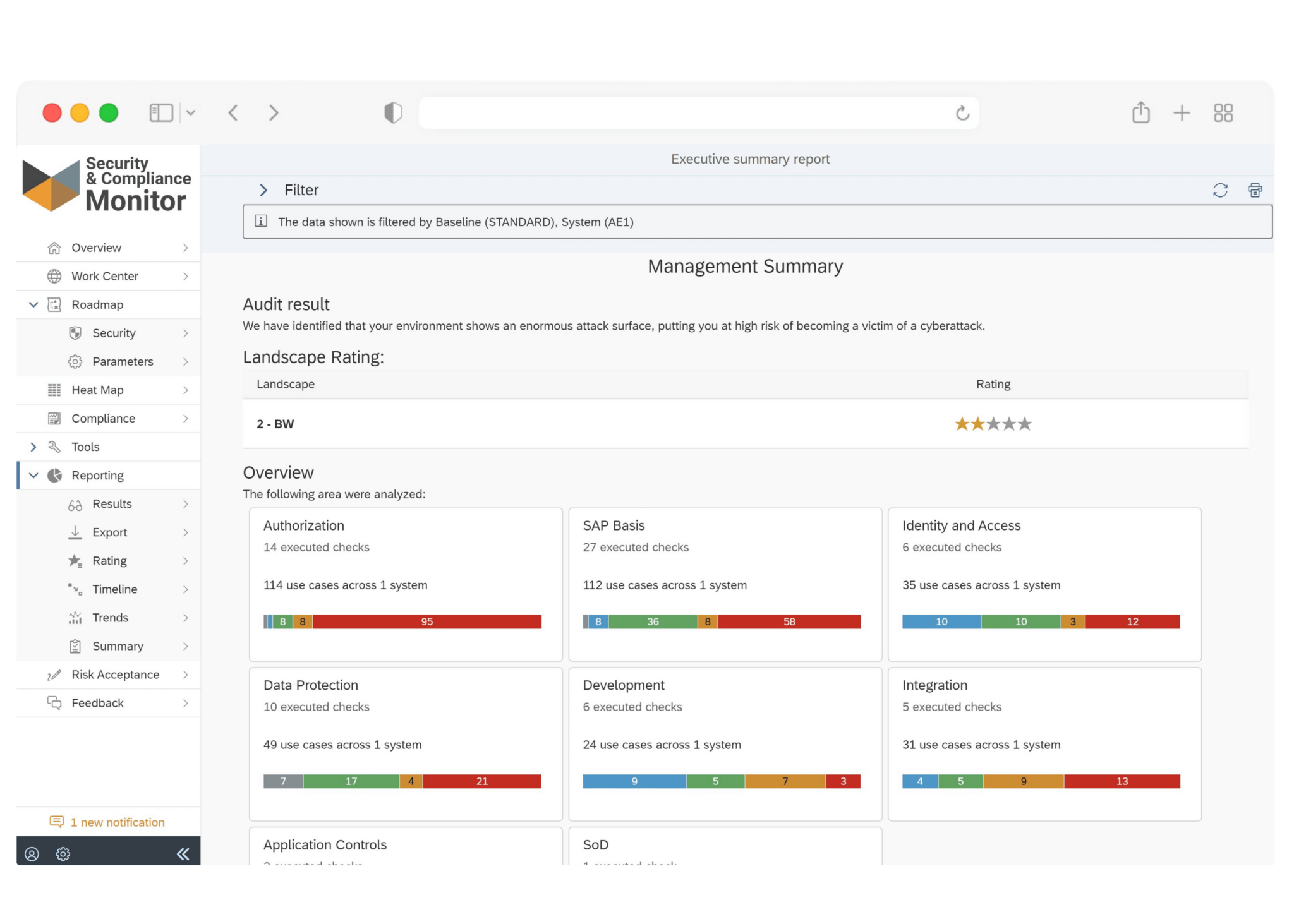
Frequently Asked Questions
What aspects are included in the scope of SAP security testing?
The scope of SAP security testing encompasses roles and authorization review, transaction monitoring, vulnerability and patch management, code security, and transport security. Covering these areas is essential to ensure a comprehensive assessment of your SAP system while adhering to a cybersecurity framework.
How does transaction monitoring contribute to SAP security?
Transaction monitoring enhances SAP security by analyzing transaction processes and identifying unusual activities that may signal breaches. This proactive approach helps safeguard sensitive data and maintain system integrity.
What is the significance of compliance testing in SAP security?
Compliance testing is crucial in SAP security as it ensures that systems meet industry regulations and the chosen best cybersecurity framework for data protection, thereby safeguarding sensitive information and maintaining organizational integrity.
Why is regular patch management important for a SAP system?
Regular patch management is crucial for the business-critical SAP systems because it mitigates security vulnerabilities and safeguards against emerging threats. Implementing timely updates ensures the integrity and reliability of your SAP systems.
What role does custom code security play in SAP security testing?
Custom code security is crucial in SAP security testing. It identifies and mitigates vulnerabilities in custom ABAP code, ensuring the overall security of the system. This proactive approach helps prevent potential exploits and enhances the integrity of SAP applications, SAP servers, and more.

Download the White Paper “Which cybersecurity framework is the best fit for SAP application security?” to learn more about the available frameworks, the challenges when adopting a framework, and more.
